How To Remove A Nose Stud With A Flat Back
| Earrings | |
|---|---|
 Types of earring: ane) helix/cartilage ii) industrial three) rook four) daith 5) tragus 6) snug vii) conch 8) anti-tragus 9) lobe | |
| Location | Ear |
| Jewelry | Captive bead ring, barbell, circular barbell, mankind plug |
| Healing | 6–12 months |
An earring is a piece of jewelry attached to the ear via a piercing in the earlobe or some other external part of the ear (except in the example of clip earrings, which clip onto the lobe). Earrings accept been worn by people in different civilizations and historic periods, ofttimes with cultural significance.
Locations for piercings other than the earlobe include the rook, tragus, and beyond the helix (come across image at correct). The simple term "ear piercing" unremarkably refers to an earlobe piercing, whereas piercings in the upper office of the external ear are often referred to equally "cartilage piercings". Cartilage piercings are more complex to perform than earlobe piercings and take longer to heal.[1]
Earring components may be made of whatsoever number of materials, including metal, plastic, drinking glass, precious stone, chaplet, wood, os, and other materials. Designs range from small loops and studs to large plates and dangling items. The size is ultimately limited by the concrete capacity of the earlobe to hold the earring without fierce. All the same, heavy earrings worn over extended periods of time may atomic number 82 to stretching of the earlobe and the piercing.
History [edit]




Silla-flow Korean earrings (6th century)

11th century Iranian earrings with pendant chains. Iranian origins confirmed by the reflexive-spiral last. Khalili Collection.

A fresco depicting an elegantly dressed woman with hoop earrings from Akrotiri, Thera (Cyclades) Greece, c. 1650-1625 BCE.[2]
Ear piercing is one of the oldest known forms of trunk modification, with creative and written references from cultures around the world dating back to early history.[iii] Gilt earrings, forth with other jewelry made of gold, lapis lazuli, and carnelian were found in the ancient sites in Lothal, Republic of india,[four] and Sumerian Royal Cemetery at Ur from the Early Dynastic period.[v] [6] [vii] Gold, silver and statuary hoop earrings were prevalent in the Minoan Culture (2000–1600 BCE) and examples tin can be seen on frescoes on the Aegean island of Santorini, Greece. During the belatedly Minoan and early Mycenaean periods of Bronze Historic period Hellenic republic hoop earrings with conical pendants were fashionable.[viii] Early evidence of earrings worn past men can be seen in archeological evidence from Persepolis in ancient Persia. The carved images of soldiers of the Farsi Empire, displayed on some of the surviving walls of the palace, show them wearing an earring.
Howard Carter writes in his description of Tutankhamun'due south tomb that the Pharaoh's earlobes were perforated, but no earrings were inside the wrappings, although the tomb independent some. The burial mask's ears were perforated as well, merely the holes were covered with golden discs. That implies that at the time, earrings were only worn in Egypt by children, much like in Egypt of Carter's times.[nine]

Other early on prove of earring-wearing is evident in the Biblical record. In Exodus 32:i–4, it is written that while Moses was upwardly on Mount Sinai, the Israelites demanded that Aaron make a god for them. It is written that he allowable them to bring their sons' and daughters' earrings (and other pieces of jewelry) to him in order that he might comply with their demand (c. 1500 BCE). By the classical period, including in the Eye Eastward, as a general rule, they were considered exclusively female ornaments. In Greece and Rome also, earrings were worn mainly by women, and the wearing of them past a human was often spoken of equally distinctively oriental.[10]
The exercise of wearing earrings was a tradition for Ainu men and women,[11] but the Government of Meiji Nippon forbade Ainu men to wearable earrings in the late-19th century.[12] Earrings were also commonplace amongst nomadic Turkic tribes and Korea. Lavish ear ornaments accept remained pop in Bharat from aboriginal times to the present day. And it was common that men and women wear earrings during Silla, Goryeo to Joseon.
In Western Europe, earrings became stylish amidst English courtiers and gentlemen in the 1590s during the English Renaissance. A document published in 1577 by clergyman William Harrison, Description of England, states "Some lusty courtiers and gentlemen of courage do wear either rings of aureate, stones or pearls in their ears."[ citation needed ] Among sailors, a pierced earlobe was a symbol that the wearer had sailed around the globe or had crossed the equator.[thirteen]
By the late 1950s or early 1960s, the exercise re-emerged in the Western world. Teenage girls were known to hold ear piercing parties, where they performed the procedure on one another. By the mid-1960s, some physicians offered ear piercing as a service.[ citation needed ] Simultaneously, Manhattan jewelry stores were some of the primeval commercial, non-medical locations for getting an ear piercing.[ citation needed ]
In the late 1960s, ear piercing began to make inroads amidst men through the hippie and gay communities, although they had been popular amongst sailors for decades (or longer).[xiv]

An ear cuff

A lobe and industrial piercing
By the early 1970s, ear piercing was common amid women, thus creating a broader market place for the procedure. Department stores throughout the country would hold ear piercing events, sponsored past earring manufacturers. At these events, a nurse or other trained person would perform the process, either pushing a sharpened and sterilized starter earring through the earlobe by hand, or using an ear-piercing instrument modified from the blueprint used past physicians.[ citation needed ]
In the belatedly 1970s, apprentice piercings, sometimes with safety pins or multiple piercings, became pop in the punk rock community. By the 1980s, the trend for male popular music performers to have pierced ears helped institute a fashion trend for men. This was later adopted past many professional athletes. British men started piercing both ears in the 1980s; George Michael of Wham! was a prominent example. During wham! he often wore pocket-size gold hoop earrings. When he and then went on the go a solo creative person with his iconic debut album "Organized religion" he wore a cross earring on his left ear. As of now, it is widely adequate for teenage and pre-teen boys to accept both ears pierced every bit well but as a manner argument.

Newborn baby girl with triple ear piercings – Costa Rica 2022.
Multiple piercings in ane or both ears get-go emerged in mainstream America in the 1970s. Initially, the trend was for women to wear a second set of earrings in the earlobes, or for men to double-pierce a single earlobe. Asymmetric styles with more and more piercings became popular, somewhen leading to the cartilage piercing trend. Double ear piercing in newborn babies is a phenomenon in Central America, in item in Costa Rica.
A variety of specialized cartilage piercings have since become popular. These include the tragus piercing, antitragus piercing, rook piercing, industrial piercing, helix piercing, orbital piercing, daith piercing, and conch piercing. In addition, earlobe stretching, while common in ethnic cultures for thousands of years, began to appear in Western society in the 1990s, and is now a adequately common sight. However, these forms of ear piercing are nonetheless infrequent compared to standard ear piercing.
Religious [edit]
According to Hindu dharma tradition, most girls and some boys (especially the "twice-born") get their ears pierced as function of a Dharmic rite known every bit Karnavedha before they are nigh five years old. Infants may get their ears pierced as early every bit several days after their nascence.
Similar customs are skillful in other Asian countries, including Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Laos, although traditionally about males wait to get their ears pierced until they have reached young machismo.
Ear piercing is mentioned in the Bible in several contexts. The most familiar refers to a Hebrew slave who was to be freed in the 7th yr of servitude simply wishes to continue serving his master and refuses to go complimentary: "…his master shall accept him before God. He shall be brought to the door or the doorpost, and his primary shall pierce his ear with an awl, and he shall then remain his slave for life" (Exodus 21:vi).
Types of earrings [edit]
Modern standard pierced earrings [edit]
Statement earrings [edit]
Statement earrings can be defined as "earrings which invite attention from others past demonstrating bold, original, and unique designs with innovative construction and textile combinations". They include ane or more than of the following design features:

Pair of starter stud earrings.
- Dangles
- Tassels
- Sparkles
- Bold or striking colours
- Hoops

Driblet earring in Full Persian 6-in-1 chainmail weave
Stud/minimal earrings [edit]
The main characteristic of stud earrings is the appearance of floating on the ear or earlobe without a visible (from the front) point of connection. Studs are invariably synthetic on the end of a post, which penetrates straight through the ear or earlobe. The post is held in identify by a removable friction back or clutch (besides known as a butterfly scroll). A stud earring features a gemstone or other decoration mounted on a narrow mail that passes through a piercing in the ear or earlobe, and is held in place by a fixture on the other side. Studs commonly come in the course of solitaire diamonds. Some stud earrings are constructed then that the post is threaded, allowing a screw dorsum to hold the earring in place securely, which is useful in preventing the loss of expensive earrings containing precious stones, or fabricated of precious metals.
Hoop earrings [edit]
Hoop earrings are circular or semi-circular in design and await very similar to a band. Hoop earrings by and large come in the form of a hoop of metal that can be opened to laissez passer through the ear piercing. They are oftentimes constructed of metal tubing, with a sparse wire attachment penetrating the ear. The hollow tubing is permanently fastened to the wire at the front of the ear, and slips into the tube at the dorsum. The entire device is held together by tension betwixt the wire and the tube. Other hoop designs do not complete the circle, simply penetrate through the ear in a post, using the aforementioned attachment techniques that apply to stud earrings. A variation is the continuous hoop earring. In this blueprint, the earring is constructed of a continuous piece of solid metal, which penetrates through the ear and can be rotated nigh 360°. One of the ends is permanently attached to a small piece of metallic tubing or a hollow metal bead. The other end is inserted into the tubing or dewdrop, and is held in identify past tension. 1 special blazon of hoop earring is the sleeper earring, a circular wire normally made of gold, with a diameter of approximately one centimeter. Hinged sleepers, which were common in Britain in the 1960s and 1970s, comprise two semi-round gold wires connected via a tiny hinge at one terminate, and fastened via a small clasp at the other, to class a continuous hoop whose fastening mechanism is effectively invisible to the naked eye. Because their modest size makes them unobtrusive and comfy, and because they are normally otherwise unadorned, sleepers are then-called because they were intended to be worn at night to keep a pierced ear from endmost, and were often the choice for the starting time set of earrings immediately post-obit the ear piercing in the decades before ear-piercing guns using studs became commonplace, only are oft a fashion option in themselves because of their attractive simplicity and because they subtly phone call attending to the fact that the ear is pierced.
A drop earring attaches to the earlobe and features a gemstone or decoration that dangles down from a chain, hoop, or similar object. The length of these ornaments vary from the very short to the extravagantly long. Such earrings are occasionally known as droplet earrings, dangle earrings, or pendant earrings. They besides include chandelier earrings, which branch out into elaborate, multi-level pendants.
Dangle earrings [edit]

Dangle earrings (also known as drop earrings) are designed to append from the bottoms of the earlobes. Their lengths vary from a centimeter or two, all the style to brushing the wearer's shoulders. A pierced dangle earring is mostly attached to the ear with a thin wire passing through the earlobe . It may connect to itself with a pocket-sized hook at the back, or in the French hook pattern, the wire passes through the earlobe piercing without closure, although pocket-size plastic or silicone retainers are sometimes used on ends. Rarely, dangle earrings use the post zipper design. There are likewise variants that attach without piercing.
Barbell earrings [edit]
Barbell earrings become their name from their resemblance to a barbell, generally coming in the form of a metallic bar with an orb on either end. Ane of these orbs is affixed in place, while the other can be detached to allow the barbell to exist inserted into a piercing. Several variations on this bones pattern exist, including barbells with curves or angles in the bar of the earring.
Huggy earrings [edit]
Commonly, stones are aqueduct set in huggy earrings.
Ear thread [edit]
Or earthreader, ear string, threader, a chain that is thin enough to slip into the ear hole, and come up back out, dangles. Sometimes, people add chaplet or other materials onto the chain, so the chain dangles with chaplet beneath the ear.
Jhumka Earrings [edit]
A type of dangling bell-shaped traditional earrings more often than not worn by women of Indian Subcontinent.
Chandelier Earrings [edit]
These earrings have an advent like to that of chandeliers. These are by women in the Indian subcontinent for special occasions.[15] [sixteen] [17]
Body piercing jewelry used as earrings [edit]

A navel curve used as an earring with a green gemmed ear stud higher up it
Body piercing jewelry is often used for ear piercings, and is selected for a diversity of reasons including the availability of larger gauges, amend piercing techniques, and a disdain for mainstream jewelry.
- Captive dewdrop rings – Captive bead rings, ofttimes abbreviated equally CBRs and sometimes called ball closure rings, are a style of trunk piercing jewelry that is an almost 360° ring with a small-scale gap for insertion through the ear. The gap is closed with a small bead that is held in place past the ring's tension. Larger approximate ball closure rings showroom considerable tension, and may require ring expanding pliers for insertion and removal of the bead.
- Barbells – Barbells are composed of a sparse, straight metal rod with a bead permanently stock-still to one terminate. The other terminate is threaded, either externally or tapped with an internal thread, and the other dewdrop is screwed into identify after the barbell is inserted through the ear. Since the threads on externally threaded barbells tend to irritate the piercing, internal threads have go the most mutual diversity. Another variation are threadless barbells or printing-fit jewelry, with a hollow mail service, a fixed back disk and a front end that is attached with a slightly bend pin that is inserted into the post.[18]
- Circular barbells – Circular Barbells are like to ball-closure rings, except that they have a larger gap, and have a permanently fastened dewdrop at one stop, and a threaded bead at the other, like barbells. This allows for much easier insertion and removal than with ball closure rings, but at the loss of a continuous look.
- Plugs – Earplugs are short cylindrical pieces of jewelry. Some plugs have flared ends to hold them in place, others require minor elastic safe rings (O-rings) to keep them from falling out. They are unremarkably used in large-gauge piercings.
- Flesh tunnels – Flesh tunnels, also known every bit eyelets or Bullet Holes, are similar to plugs; still, they are hollow in the heart. Flesh tunnels are most usually used in larger gauge piercings either considering weight is a concern to the wearer or for artful reasons.
-

Stretched ear piercing without jewelry
-
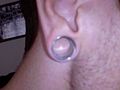
Gauges and other measuring systems [edit]
For an caption of how earring sizes are denoted, see the article Trunk jewelry sizes.
Clip-on and other non-pierced earrings [edit]

Mod lobe earring screwed onto the lobe.
Several varieties of non-pierced earrings exist.
- Prune-on earrings – Clip-on earrings take existed longer than any other diverseness of non-pierced earrings. The prune itself is a 2-part piece attached to the back of an earring. The two pieces closed around the earlobe, using mechanical pressure level to hold the earring in place.
- Magnetic earrings – Magnetic earrings simulate the look of a (pierced) stud earring past attaching to the earlobe with a magnetic back that agree the earring in place on by magnetic strength.
- Stick-on earrings – Stick-on earrings are adhesive-backed items which stick to the skin of the earlobe and simulate the look of a (pierced) stud earring. They are considered a novelty item.
- Spring hoop earrings – Bound hoops are about indistinguishable from standard hoop earrings and stay in place by means of spring force.
- An culling which is oftentimes used is bending a wire or even just using the ring portion of a CBR to put on the earlobe, which stays on by pinching the ear
- Ear hook earrings – A large hook like the fish hook that is big enough to hook and hang over the whole ear and dangles.
- The hoop – A hoop threads over the ear and hangs from just within the ear, in a higher place where ears are pierced. Mobiles or other dangles can be hung from the hoop to create a variety of styles.
- Ear screws – Screwed onto the lobe, allow for verbal adjustment—an culling for those who notice clips as well painful.
- Ear cuffs – Wrap around the outer cartilage (similar to a conch piercing) and may exist chained to a lobe piercing.
Permanent earrings [edit]
Where about earrings worn in the western world are designed to be removed easily to exist inverse at will, earrings tin also be permanent (non-removable). They were once used as a mark of slavery or ownership (e.g., see Ex.21:2–6, Deut.15:sixteen–17). They appear today in the grade of larger gauge rings which are difficult or impossible for a person to remove without aid. Occasionally, hoop earrings are permanently installed by the use of solder,[19] though this poses some risks due to toxicity of metals used in soldering and the take chances of burns from the heat involved. Besides permanent installations, locking earrings are occasionally worn due to their personal symbolism or erotic value.
Ear piercing [edit]
Pierced ears are earlobes or the cartilage portion of the external ears which have had i or more holes created in them for the wearing of earrings. The holes may be permanent or temporary. The holes become permanent when a fistula is created by scar tissue forming around the initial earring.
Piercing techniques [edit]
A variety of techniques are used to pierce ears, ranging from "practice information technology yourself" methods using household items to medically sterile methods using specialized equipment.
A long-continuing home method involves using ice every bit a local anesthetic, a sewing needle as a puncture musical instrument, a burning match and rubbing alcohol for disinfection, and a semi-soft object, such as a potato, cork, bar of soap or condom eraser, as a button point. Sewing thread may exist fatigued through the piercing and tied, equally a device for keeping the piercing open during the healing process. Alternatively, a gold stud or wire earring may be directly inserted into the fresh piercing as the initial retaining device. Home methods are ofttimes unsafe and risky due to issues of improper sterilization or placement.
Another method for piercing ears, offset made popular in the 1960s, was the use of sharpened bound-loaded earrings known as self-piercers, trainers, or sleepers, which gradually pushed through the earlobe. All the same, these could skid from their initial placement position, oft resulting in more discomfort, and many times would not go all the way through the earlobe without additional force per unit area being applied. This method has fallen into decay due to the popularity of faster and more successful piercing techniques.

An ear beingness pierced with an ear piercing instrument
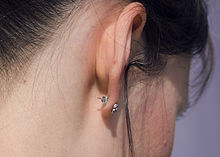
Pierced ear with traditional starter stud
Ear piercing instruments, sometimes called ear-piercing guns, were originally developed for doctor use but with modifications became available in retail settings.[twenty] Today more and more people in the Western world accept their ears pierced with an ear piercing instrument in specialty jewellery or accompaniment stores, or at dwelling house using disposable ear piercing instruments. An earlobe piercing performed with an ear piercing musical instrument is often described equally feeling similar to beingness pinched, or existence snapped by a rubber band. Piercing with this method, specially for cartilage piercings, is not recommended past many piercing professionals and physicians, every bit it can cause blunt forcefulness trauma to the skin, and takes far longer to heal than needle piercing. In addition, the vast majority of ear piercing instruments are made of plastic, which ways they tin never be truly sterilized by use of an Autoclave, increasing chance of infection exponentially. In the case of cartilage piercing, doing it with an ear piercing instrument can shatter the ear cartilage and lead to serious complications.
An culling which is growing in practice is the use of a hollow piercing needle, as is done in body piercing. The piercer disinfects the earlobe with booze and puts a mark on the lobe with a pen. It gives the opportunity to the customer to bank check whether the position is right or not. Then, the piercer uses a clamp with flat ends and holes at the end to concur the earlobe, with the dot in the middle of the holes. This device will back up the skin during the piercing process. A cork tin exist placed behind the earlobe to finish the movement of the needle after the piercing process, and protect the tip of the needle for the client's comfort. And so, the piercer places the hollow needle perpendicular to the skin'south surface and bank check the position of the needle, to pierce at the desired identify and the right angle. The piercing process consists of pushing the needle through the earlobe, until information technology gets out in the other side. The client has to remain all the same during all the process. Then, the clamp can be put off. After that, the piercer puts the gem in the hollow needle and pushes the needle through until the jewel enters into the lobe. Then, the needle is removed and tending properly. The gem is attached to the lobe and the piercer disinfects the lobe again.
In tribal cultures and among some neo-primitive body piercing enthusiasts, the piercing is made using other tools, such as animal or institute organics.
Initial healing time for an earlobe piercing performed with an ear piercing instrument is typically half-dozen to viii weeks. After that fourth dimension, earrings can be changed, but if the hole is left unfilled for an extended period of time, there is some take chances of the piercing closing. Piercing professionals recommend wearing earrings in the newly pierced ears for at to the lowest degree six months, and sometimes even a full year. Cartilage piercing will usually require more healing time than earlobe piercing, sometimes ii to iii times as long. Later healing, earlobe piercings will shrink to smaller gauges in the prolonged absenteeism of earrings, and in most cases volition completely disappear.
Health risks [edit]
The health risks with conventional earlobe piercing are common but tend to be small, particularly if proper technique and hygienic procedures are followed. One report found that upward to 35 percent of persons with pierced ears had 1 or more complications, including modest infection (77 percent of pierced ear sites with complications), allergic reaction (43 pct), keloids (2.5 percent), and traumatic tearing (two.five percent).[21] Pierced ears are a significant risk factor for contact allergies to the nickel in jewelry.[22] Earlobe tearing, during the healing period or after healing is consummate, tin can be minimized by non wearing earrings, especially wire-based dangle earrings, during activities in which they are probable to become snagged, such every bit while playing sports. As well, larger gauge jewellery volition lessen the chance of the earring being torn out.[ commendation needed ]
With cartilage piercing, the blunt force of an ear piercing instrument will traumatize the cartilage, and therefore make healing more than hard. Also, because there is substantially less blood flow in ear cartilage than in the earlobe, infection is a much more than serious outcome. There take been several documented cases of severe infections of the upper ear following piercing with an ear piercing instrument, which required courses of antibiotics to clear up. There are many ways that an infection can occur: the most common way is when the person that got pierced decides to take out the piercing likewise early on. According to the A.M.A.[23] [ failed verification ] the proper waiting period to change or take out a piercing with substantially less risk of infection would be iii weeks.
For all ear piercings, the use of a sterilized hollow piercing needle tends to minimize the trauma to the tissue and minimize the chances of contracting a bacterial infection during the procedure. As with any invasive procedure, there is e'er a risk of infection from blood borne pathogens such as hepatitis and HIV. However, modern piercing techniques make this run a risk extremely minor (the gamble existence greater to the piercer than to the pierced due to the potential splash-back of blood). There has never been a documented case of HIV manual due to ear/body piercing or tattooing, although at that place accept been instances of the Hepatitis B virus beingness transmitted through these practices.[24]
- Negative effects of wearing earrings in low-cal of inquiry
The most frequent complications continued with wearing earrings are:[25]
- inflammation
- keloids
- loss of tissue by tearing
- mechanical division of earlobes
- potential skin disorder
Researchers observed a correlation between the piercing of young girls' earlobes and subsequent development of allergies.[26] [27] [28]
In Professor Ewa Czarnobilska'southward view (the manager of research squad) the main reason of allergy (listed past allergists) is presence of nickel as a component of alloys used in the product of earrings – however the ingredients alleged by producer is not meaning, because nickel is a standard component of jewellery.[27] [28]
Symptoms of allergy are visible as eczema. This symptom is frequently justified to exist food allergy (e.chiliad. to milk), meanwhile the reason is contact with the earring (precisely Ni ions) with the lymphatic organization.[27] [28] Ceasing of wearing earrings by children does non result in vanishing allergy symptoms. The allowed system remembers the presence of Ni ions that existed in someone's blood and lymph. Even though the children ceased wearing earrings, it tin appear as an allergic reaction to:[27] [28]
- metal parts of wardrobe
- dental braces
- dental prosthesis
- orthotics
- meals cooked in pots with addition of nickel
- margarine (nickel is a catalyst in hydrogenation of unsaturated fats)
- coins
- chocolate
- nuts
- leguminous vegetables
- wine
- beer
Research studying a sample of 428 pupils, age seven and 8, and sixteen and seventeen noticed that:[27] [28]
- thirty percent of population were allergic to nickel
- allergy occurred for many girls who had started wearing earrings in early childhood.
Other symptoms of allergy to nickel are:[27] [28]
- recurring infections
- asthma attacks
- chronic larynxis
See also [edit]
- Jewelry wire gauge
References [edit]
- ^ Davis, Jeanie. "Piercing? Stick to Earlobe". WebMD. WebMD. Retrieved 5 January 2022.
- ^ Kleiner, Fred Southward. (2015). Gardner'southward Art through the Ages: Backpack Edition, Book A: Antiquity. [ ]: Cengage Learning. pp. 90–91. ISBN9781305544895.
2 elegantly dressed young women bedecked with bracelets and hoop earrings get together crocuses. […] Crocus gatherers, detail of the east wall of room 3 of building Xeste 3, Akrotiri, Thera (Cyclades) Greece, c. 1650-1625 BCE
- ^ Administrator (2014-04-11). "A Historical Look at Body Piercings". Kolo Piercing . Retrieved 2021-07-22 .
- ^ Ornament in Indian Architecture. Academy of Delaware Press. 1991. p. xiv. ISBN9780874133998.
- ^ "Earring — ca. 2600–2500 B.C." MetMuseum.org . Retrieved 2020-03-06 .
- ^ "Jewelry from The Royal Tombs of Ur". sumerianshakespeare.com . Retrieved 2020-03-06 .
- ^ "Queen Puabi'south Headdress from the Regal Cemetery at Ur - Penn Museum". world wide web.penn.museum . Retrieved 2020-03-06 .
- ^ Pitts-Taylor, Victoria (2008). Cultural Encyclopedia of the Body [ii volumes]. [ ]: ABC-CLIO. pp. 94–95. ISBN9781567206913.
The Fayum mummy portraits from Hawara dating from the beginning to the third centuries CE draw several females with various styles of earrings. In about cases, the portraits are thought to correspond Greek colonists living in Egypt. Some early Greeks wore earrings for the purposes of fashion as well as protection against evil. The popularity of earrings is evident in major cultures of the ancient world. In the centre Minoan period (2000–1600 BCE), gilded, argent, and statuary hoop earrings with tapered ends were popular. In the late Minoan and early Mycenaean periods, the hoop evolved with a conical pendant.
- ^ The Tomb of Tut-Ankh-Amen: Discovered by the Late Earl of Carnarvon and Howard Carter, Book 3, pp. 74–75
- ^ Chisholm 1911, p. 798.
- ^ Sherrow, Victoria (2001). For appearance' sake: the historical encyclopedia of skilful looks, dazzler, and grooming. Greenwood Publishing Group via Google Books. p. 101.
- ^ Ito, Masami (May 20, 2008). "Ainu: ethnic in every way just not by official fiat". The Japan Times. Retrieved March 4, 2022.
- ^ Demello, Margo (2007). Encyclopedia of torso beautification. ISBN978-0-313-33695-nine.
- ^ Hall, Trish (1991-05-19). "Piercing Fad Is Turning Convention on Its Ear". The New York Times.
- ^ https://in.pinterest.com/praveenjaipurmart/chandlier-earrings/
- ^ "eleven Chandelier Earrings For Weddings & All Kinds Of Brides".
- ^ https://www.eindiawholesale.com/blog/post/famous-hollywood-celebs-dear-indian-mode.html
- ^ The Piercing Bible: The Definitive Guide to Prophylactic Body Piercing, Elayne Angel Potter/X Speed/Harmony/Rodale, 16 February 2022, p72
- ^ "No earrings give Cordone midas touch". BBC News. 2000-08-27. Retrieved 2008-06-09 .
- ^ Erica Weir (2001-03-20). "Canadian Medical Clan Journal – Omphalus gazing: a clinical glimpse at body piercing". CMAJ. 164 (6): 864. PMC80907. PMID 11276561. Retrieved 2012-06-10 .
- ^ Meltzer DI (2005). "Complications of body piercing". Am Fam Physician. 72 (10): 2029–34. PMID 16342832. Archived from the original on 2008-05-16. Retrieved 2008-01-29 .
- ^ Thyssen JP, Linneberg A, Menné T, Johansen JD (2007). "The epidemiology of contact allergy in the general population—prevalence and main findings". Contact Dermatitis. 57 (5): 287–99. doi:ten.1111/j.1600-0536.2007.01220.10. PMID 17937743. S2CID 44890665.
- ^ "American Medical Clan". Ama-assn.org. Retrieved 2012-06-x .
- ^ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. "CDC Fact Sheet: HIV and Its Transmission". Cdc.gov. Archived from the original on 2022-06-07. Retrieved 2012-06-10 .
- ^ Watson D. (Feb 2022). "Torn Earlobe Repair". Liver International. 35 (1): 187.
- ^ Harmful earrings (pl. Szkodliwe kolczyki) Fizjointormator. Retrieved 2022-04-01
- ^ a b c d due east f "Polscy naukowcy ostrzegają: kolczyki szkodzą dzieciom" [Polish scientists warn: earrings harm children]. TVN24.pl (in Polish). 2022-08-26. Retrieved 2015-04-01 .
- ^ a b c d e f Czarnobilska E.; Oblutowicz K.; Dyga Westward.; Wsołek-Wnek G.; Śpiewak R. (May 2009). "Contact hypersensitivity and allergic contact dermatitis amongst school children and teenagers with eczema". Contact Dermatitis. 60 (v): 264–269. doi:x.1111/j.1600-0536.2009.01537.x. PMID 19397618. S2CID 30920753.
Further reading [edit]
- Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. viii (11th ed.). Cambridge University Printing. pp. 798–799. This source has a summary description of archaeological and artistic finds as of the early on 20th century.
- van Cutsem, Anne, A World of Earrings: Africa, Asia, America, Skira, 2001. ISBN 88-8118-973-9
- Holmes, Anita, Pierced and Pretty: The Complete Guide to Ear Piercing, Pierced Earrings, and How to Create Your Own, William Morrow and Co., 1988. ISBN 0-688-03820-4
- Jolly, Penny Howell, "Marked Difference: Earrings and 'The Other' in Fifteenth-Century Flemish Artwork," in Encountering Medieval Textiles and Clothes: Objects, Texts, Images, Palgrave Macmillan, 2002, pp. 195–208. ISBN 0-312-29377-1
- Mascetti, Daniela and Triossi, Amanda, Earrings: From Antiquity to the Nowadays, Thames and Hudson, 1999. ISBN 0-500-28161-0
- McNab, Nan, Body Bizarre Torso Beautiful, Fireside, 2001. ISBN 0-7432-1304-1
- Mercury, Maureen and Haworth, Steve, Pagan Fleshworks: The Alchemy of Body Modification, Park Street Press, 2000. ISBN 0-89281-809-three
- Steinbach, Ronald D., The Fashionable Ear: A History of Ear Piercing Trends for Men and Women, Vantage Press, 1995. ISBN 0-533-11237-0
- Vale, V., Modern Primitives, RE/Search, 1989. ISBN 0-9650469-three-ane
External links [edit]
How To Remove A Nose Stud With A Flat Back,
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Earring
Posted by: wilsonlaze1943.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Remove A Nose Stud With A Flat Back"
Post a Comment